The Power of Secondary Dimensions in Search Engine Optimization: Maximizing Your Insights
The Power of Secondary Dimensions in Search Engine Optimization: Maximizing Your Insights
Blog Article
Enhance Your Information Analysis Using Second Measurements
In the world of information evaluation, key metrics often supply a foundational understanding of efficiency or patterns. The true depth of understandings lies in the integration of additional measurements. These extra layers of information offer a nuanced view that can untangle subtleties and intricacies not apparent at very first look. The capacity to dissect details with various lenses opens up doors to a realm of possibilities that can change just how companies act and analyze upon their data. The calculated use of secondary dimensions raises evaluation past the surface degree, assuring a wealth of untapped possible waiting to be found.
Comprehending Additional Measurements
Second measurements in information evaluation refer to added attributes or metrics that supply deeper insights when integrated with main information dimensions, boosting the general understanding of the dataset. These extra measurements supply a more comprehensive view of the data, allowing analysts to uncover concealed patterns, relationships, and fads that might not appear when just taking into consideration main measurements.
By including secondary measurements into information analysis, analysts can get an extra nuanced understanding of the elements influencing the key metrics. In marketing analysis, key measurements could include basic client demographics like age and sex, while secondary dimensions can encompass variables such as acquiring habits, preferences, or geographical location. By combining these secondary and main measurements, analysts can produce more in-depth client profiles, enabling even more targeted and effective advertising and marketing methods.
Additionally, second measurements can assist in recognizing connections between various variables, leading to more accurate anticipating modeling and decision-making. They enable experts to explore data from several point of views, enhancing the understandings drawn from the dataset and inevitably improving the high quality of evaluation and strategic suggestions.
Benefits of Second Measurements
When thinking about data evaluation, integrating secondary dimensions supplies a plethora of advantages that substantially enhance the deepness and breadth of understandings acquired from key information measurements. Among the crucial advantages of additional measurements is the capability to supply context to main information. By including second dimensions such as time, area, or group information to the evaluation, scientists can gain an extra comprehensive understanding of the key information points - secondary dimensions. This contextual details can aid identify patterns, fads, and relationships that might have or else gone undetected.
In addition, additional dimensions can additionally help in segmenting data, permitting an extra thorough evaluation of details parts within the primary information. This division can cause more targeted techniques and actions based on the one-of-a-kind features of each section. In addition, additional measurements can help in verifying findings from main information measurements, giving an extra reliable and durable basis for decision-making.
Essentially, the benefits of incorporating second dimensions into data evaluation are very useful, using richer insights and allowing more educated decision-making processes.
Executing Additional Dimensions Successfully
When incorporating secondary dimensions, it is vital to align them with the primary measurements to obtain deeper insights right into the data. It is crucial to select additional i thought about this dimensions that complement the main information without triggering noise or complication in the analysis.
Furthermore, take into consideration the scalability of the secondary measurements across various datasets or analyses. Guarantee that the selected additional dimensions can be consistently applied and analyzed across various circumstances to preserve the honesty and uniformity of the analysis. Furthermore, establish an organized process for integrating secondary dimensions right into the website here evaluation workflow to streamline the analysis of outcomes. By carrying out second measurements efficiently, analysts can improve the depth and accuracy of their information evaluation, causing more educated decision-making and workable insights.
Advanced Techniques With Additional Measurements
For an extra sophisticated strategy to information evaluation, integrating second measurements can considerably elevate the depth of understandings gained. Advanced strategies with second measurements entail even more elaborate techniques to extract valuable details from data collections. One such strategy is cohort evaluation, where data is fractional based on particular features or behaviors to track patterns over time. This approach enables for a much deeper understanding of just how various teams progress and communicate with your service or product.
One more innovative method is regression analysis, which helps determine connections between variables and exactly how they affect each various other. By adding additional dimensions, such as demographic info or user habits, to regression designs, you can reveal more nuanced insights and make more exact predictions.
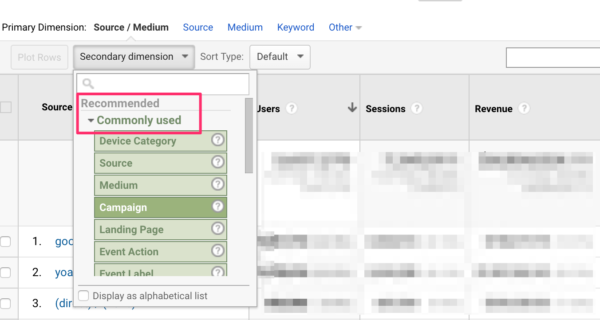
Case Researches: Additional Measurements in Action
In one more circumstance, a doctor leveraged additional measurements to maximize resource allocation. By evaluating person results in connection with geographical place, the company recognized locations with high readmission prices. This resulted in the implementation of targeted intervention programs in those regions, ultimately boosting client care and lowering medical care expenses.
These instance researches highlight the power of secondary dimensions in uncovering useful insights that drive calculated decision-making. By diving deeper right into data evaluation beyond primary metrics, companies can obtain a much more comprehensive understanding of their clients more information and procedures, resulting in more efficient and informed business approaches.
Final Thought
In final thought, the unification of additional dimensions in information analysis is important for gaining a thorough understanding of underlying factors and trends. By utilizing strategies such as cohort evaluation and regression analysis, organizations can reveal hidden understandings and make more informed choices. Secondary dimensions include depth and breadth to information evaluation, enabling businesses to discover data from numerous viewpoints and drive much more effective results.
In marketing evaluation, main measurements might include standard client demographics like age and gender, while second dimensions can include variables such as acquiring habits, preferences, or geographical area.When taking into consideration information analysis, incorporating secondary dimensions supplies a wide range of advantages that dramatically improve the depth and breadth of understandings derived from primary information dimensions.Additionally, additional measurements can likewise aid in segmenting data, enabling for a more thorough analysis of particular subsets within the main information. Furthermore, second measurements can aid in verifying findings from primary information measurements, giving an extra dependable and robust basis for decision-making.
When integrating additional dimensions, it is vital to straighten them with the primary dimensions to get deeper insights right into the information.
Report this page